This article was contributed by Dr Gayaithiri Ramasandran, Consultant Obstetrics & Gynaecology (O&G) at Pantai Hospital Cheras.
To book an appointment or learn more about Dr Gayaithiri Ramasandran and her clinic, click here.
What is PCOS?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder among females of reproductive age worldwide affecting between 5% and 26% of females. Up to 70% of affected women remain undiagnosed worldwide. PCOS can be as common as being present in 1 in 4 women between the ages of 18 to 35 years. PCOS is a condition in combination of various metabolic disorder and hormonal imbalance, including elevated androgen levels in many patients.
Common Sign and Symptoms
- Irregular menses or no menses at all
- Infertility - difficulty getting pregnant
- Hirsutism - excessive hair growth
- Weight gain
- Thinning of hair or hair loss
- Acne
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. It is a multifactorial condition which includes insulin resistance, hormonal imbalance, excessive male hormone exposure and genetics which can run in families.
What can PCOS lead to
- PCOS is associated with multiple comorbidities:
- Infertility - Difficult to get pregnant
- Obesity
- Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance
- High cholesterol
- Hypertension
- Cardiovascular risks
- Depression
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Uterine cancer and pre-cancerous conditions - It is important to have a period every 3-4 months to reduce the risk of excessive thickening of the lining of the uterus which eventually can lead to cancer.
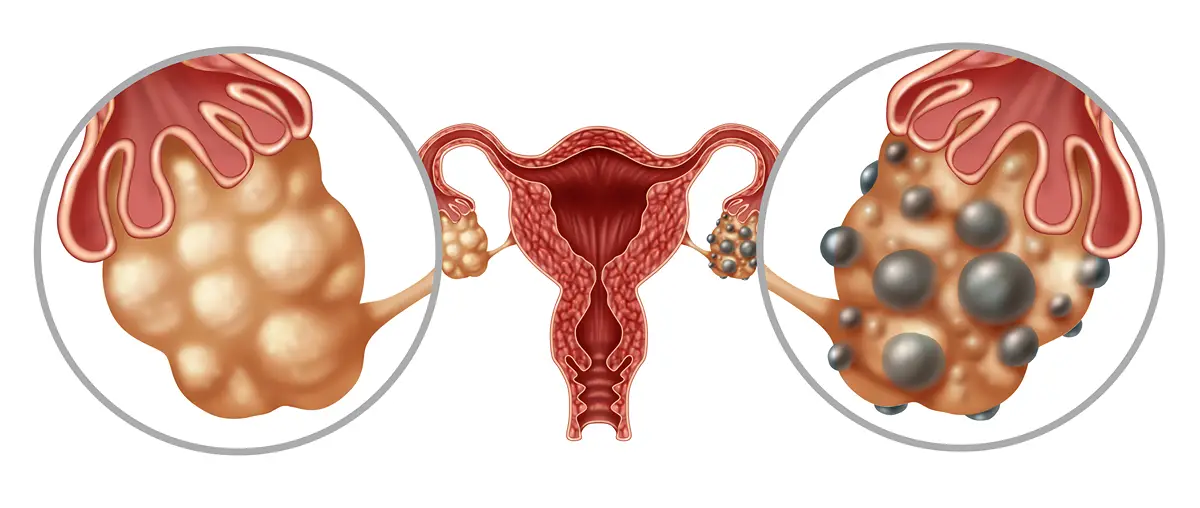
How PCOS is diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made by thoroughly assessing PCOS symptoms, doing physical exams, performing laboratory tests, and imaging. No single test can confirm or exclude the diagnosis of PCOS.
To diagnose PCOS, doctors look for the presence of at least 2 of the following 3 criteria:
- Irregular menstruation or ovulation disorder
- Excess androgen hormones (clinical or biological) - high levels of "male" hormones in your body, which may cause physical signs such as excess facial or body hair
- Polycystic ovaries - ovaries become enlarged and contain many fluid-filled sacs (follicles) that surround the eggs (but despite the name, you do not actually have cysts if you have PCOS)
Management and treatment
- Lifestyle modification is the first line management of PCOS: healthy balanced diet, exercise and weight loss as low as 5% has been noted to be helpful with the resolution of clinical symptoms.
- The benefits of balanced diet and losing weight include:
- lower risk of insulin resistance and developing diabetes
- lower risk of heart problems
- lower risk of cancer of the womb
- more regular periods
- as fertility treatments to increase chance of becoming pregnant
- reduction in acne and a decrease in excess hair growth over time
- improved mood and self-esteem.
- There is no cure for PCOS but treatments can improve symptoms.
- The treatment plan is tailored around your health goals and is individualised.
- Medications may be prescribed to regulate irregular menstrual periods, improve insulin resistance and fertility.
- Surgery such as laparoscopic ovarian drilling may be required to treat fertility problems associated with PCOS that do not respond to medicine.
PCOS Clinic ‘Near Me’ in Kuala Lumpur
Do visit a gynaecologist for accurate diagnosis and get a personalised treatment plan if you have any of the symptoms such as irregular, heavy or no menses, difficulty getting pregnant, weight gain, acne or any concern about your reproductive health.
Early detection and treatment can improve long term health risk. You can reduce this risk with a healthy lifestyle, regular health checks (e.g. blood pressure, blood glucose and ultrasound) and medicine if required. If you have any of the above-mentioned symptoms, please do not hesitate to get consultation with a Gynaecologist as soon as possible.