
Introduction
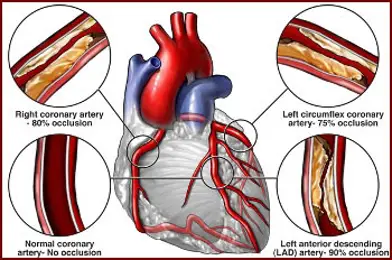
Definition
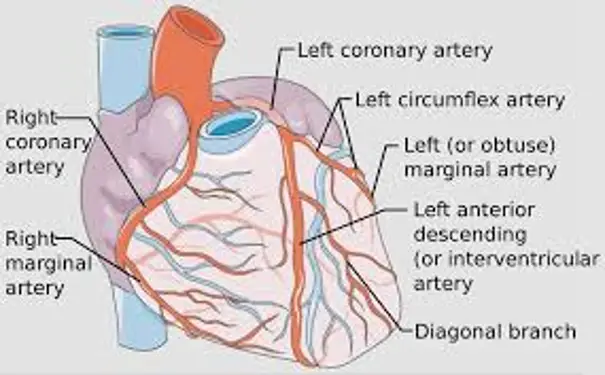
Heart Anatomy
Risk Factors of CAD
| Category | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Predisposing factors | Age, sex, family history, genes |
| Risk-modifying behaviors | Smoking, atherogenic diet, alcohol intake, physical activity |
| Metabolic risk factors | Dyslipidemias, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome |
| Disease markers | Calcium score, catheterization results, stress test results, left ventricular hypertrophy on echocardiogram, personal history of vascular disease (prior myocardial infarction or stroke, angina, peripheral vascular disease), inflammatory state |
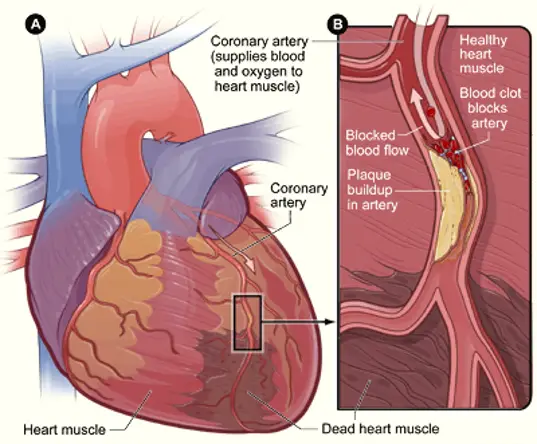
Pathophysiology
Myocardial Infarction
Symptoms
Test/Screenings to Diagnose
Management & Treatment considerations (Factors)
Management & Treatment considerations for Chronic vs Acute conditions
This article was contributed by Associate Professor Dr. Ahmad Zuhdi Bin Mamat, Resident Consultant Cardiothoracic Surgeon at Pantai Hospital Ipoh. To know more about where and when to see Associate Professor Dr. Ahmad Zuhdi Bin Mamat at his clinic, click here .

