Rheumatology Conditions and Treatment for Inflammatory Disorders
Rheumatology is the sub-speciality of medicine that focuses primarily on joints, soft tissues, connective
tissue disorders and autoimmune diseases such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, ankylosing
spondylitis, degenerative joint diseases, and vasculitis.
Rheumatologists are consultants who specialise in rheumatology.
What are the types of rheumatic diseases and their symptoms?
The most common rheumatic diseases include:
RA is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease. Autoimmune is a condition whereby your
immune system attacks and destroys healthy cells in your joints by mistake).
Symptoms include:
- Typically symmetrical swollen, stiff, and painful small joints (feet, hand, and wrist)
- It may involve larger joints
- Stiffness worsens in the morning
- Fatigue
- Poor appetite
- Fever
Learn more about common extra
articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is called a degenerative joint disease. It is the commonest form of
arthritis. Osteoarthritis mainly occurs in the knee, hips, and fingers.
Symptoms include:
- Joint pain during movements that worsens at the end of the day
- Crepitus
- Joint instability
- Joint stiffness
PsA is an autoimmune disease associated with psoriasis (a chronic skin disease). It can
affect small or large joints.
Symptoms include:
- Swollen, painful joints
- Joint stiffness
- Pain
- Rashes
- Changes in colour and texture of nails
- Fatigue
Ankylosing spondylitis is an autoimmune disease that affects the sacroiliac joints and
spine.
Symptoms include:
- Gradual onset of lower back pain that worsens at night
- Morning back stiffness
- Pain radiating to the hips and buttocks
- Fatigue
Gout develops due to the build-up of uric acid crystals within the joint. Gout usually
affects the big toe joint initially.
Symptoms include:
- Intense pain in joints like the big toe, knees, ankles, wrists, and fingers
- Red and swollen joints
- Joint stiffness
SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs and can be fatal.
Medical interventions and lifestyle modifications can help manage the disease.
Symptoms include:
- Itchy and painful rashes across cheeks (butterfly rash)
- Arthritis
- Photosensitivity (sensitivity to light)
- Oral ulcers
- Seizure
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
- Raynaud’s phenomenon - fingers and toes become white/pale or blue
A connective tissue disorder that may affect your organs, blood circulation, and skin.
Symptoms include:
- Oedematous fingers (swelling due to fluid accumulation)
- Shiny skin
- Thickening of the skin on fingers
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Telangiectasia - dilated blood vessels visible on the skin surface
- Pain while swallowing (odynophagia)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that affects moisture-producing glands
(salivary and lacrimal glands).
Symptoms include:
- Dry eyes
- Dry mouth
- Dry skin
- Vaginal dryness
- Fatigue
- Polyarthritis
- Swelling between ears and jaws (swollen salivary glands)
- Joint or muscle pain
Vasculitis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the blood vessels.
Vasculitis can present as a minor problem to a more severe condition where it affects your
entire body. Signs and symptoms of vasculitis depend on the type and severity of the
disease.
Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Body aches
What is paediatric rheumatology?
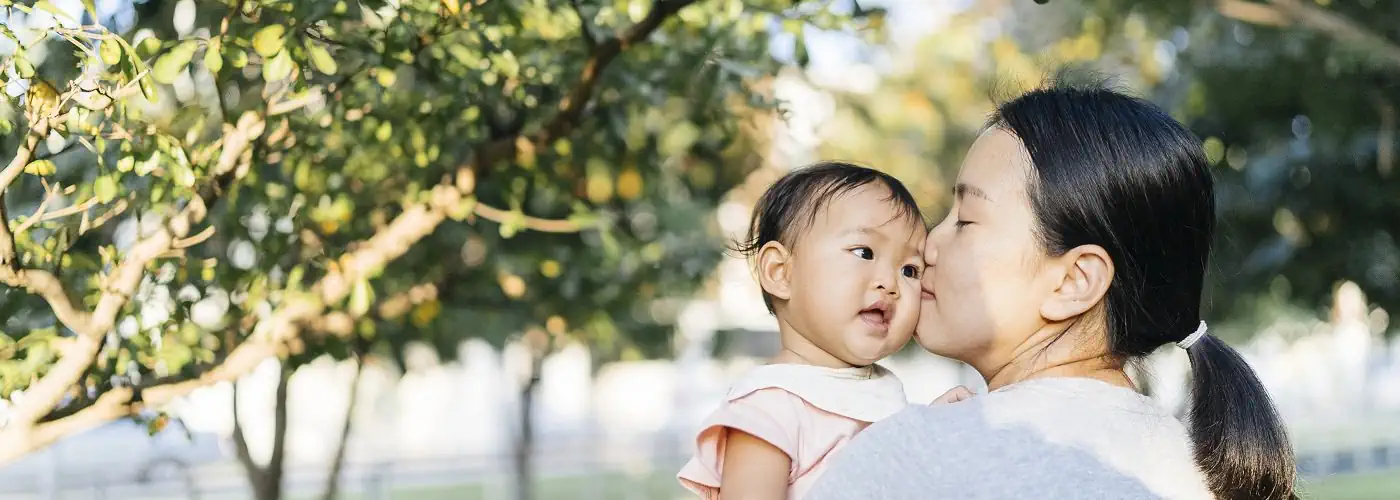

As the name implies, paediatric rheumatologists treat rheumatic diseases in children.
Commonly observed rheumatic diseases in children are:
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
- Juvenile dermatomyositis or vasculitis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Common symptoms include:
- Prolonged fever with unknown cause
- Muscle weakness
- Deformity
- Muscle weakness
- Limping
It is crucial to immediately seek medical consultation if your child complains of any of the symptoms above.
How are rheumatic diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosis is made based on various investigations. Your doctor will first evaluate your medical history and
symptoms before conducting a physical examination.
Tests that may be requested are:
- Imaging modalities: X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),
ultrasound, and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan
- Joint aspiration
- Blood tests: Rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA), antinuclear
antibodies (ANA), antiphospholipid antibodies
- Tissue biopsy
What are the treatment options for rheumatic diseases?
The treatment options differ according to the types of rheumatic diseases.
Treatments options include:
- Medications
- Analgesics: Paracetamol, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Physical and occupational therapy
- Surgery