What is Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)?
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), commonly known as stenting, is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It helps restore blood flow to the heart and reduce symptoms of coronary artery disease such as chest pain (angina).
✅How does PCI work?
🔹 A thin catheter is inserted through a
blood vessel in the groin or wrist and guided to the blockage.
🔹 A small
balloon at the catheter’s tip is inflated to widen the artery.
🔹 In most cases,
a stent (tiny metal scaffold) is placed to keep the artery open and
prevent future blockages.
Why Apply VDO Framework to PCI?
Applying the Value-Driven Outcome (VDO) framework to PCI procedures ensures better patient outcomes, cost efficiency, and standardized care. By tracking complications, readmissions, and heart health, the framework helps:
✔Improve quality and safety in heart care.
✔Reduce unnecessary
costs while optimizing resources.
✔Align PCI performance with
international best practices.
✔Enhance transparency and trust between healthcare
providers and patients.
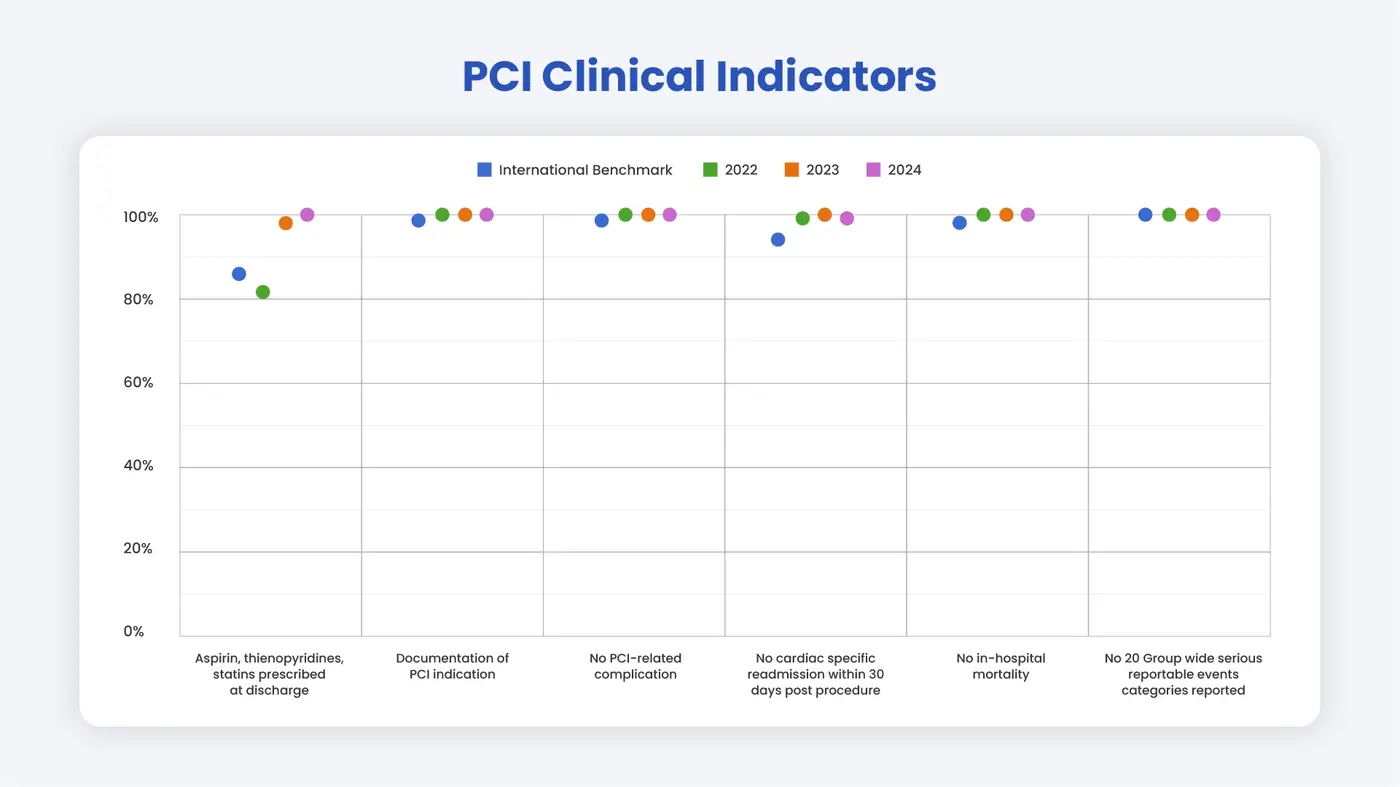
PCI Clinical Indicators
- Essential Heart Medications Prescribed at Discharge
✔ Patients should receive aspirin, thienopyridines, and statins after PCI unless medically contraindicated.
✔ These medications reduce the risk of future heart events and improve long-term survival. - Clear Documentation of PCI Indication
✔ Every PCI should have a documented medical reason (e.g., symptom relief, life-saving intervention).
✔ Proper documentation ensures transparency, improves outcomes, and supports best practices. - No PCI-Related Complications
✔ Complications increase healthcare costs and impact survival.
✔ Monitoring complication rates help identify areas for improvement and enhance patient safety. - No Cardiac-Specific Readmission Within 30 Days
✔ Readmissions after PCI could signal complications or inadequate post-procedure care.
✔ Tracking this metric helps refine treatment plans and follow-up care. - No In-Hospital Mortality
✔ Monitoring hospital mortality rates allow PHKL’s team to review and refine treatment protocols.
✔ This supports continuous quality improvement and patient safety. - No Serious Reportable Events (SREs)
✔ PHKL actively monitors, reviews, and prevents serious reportable events.
✔ By learning from past incidents, we ensure better patient safety and care excellence.
How does Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur compare to international benchmarks?





.webp?sfvrsn=20763f7d_21)



.webp?sfvrsn=f2a2c343_12)


