
Your doctor would first question your general health and symptoms before conducting a thorough physical examination.
Diagnosis is made based on your reported symptoms, physical examination, and investigations.
Common diagnostic tests are X-ray, CT scan, and MRI. Additional tests such as biopsy may be required for certain conditions to help ascertain the diagnosis.
Imaging diagnostic tests
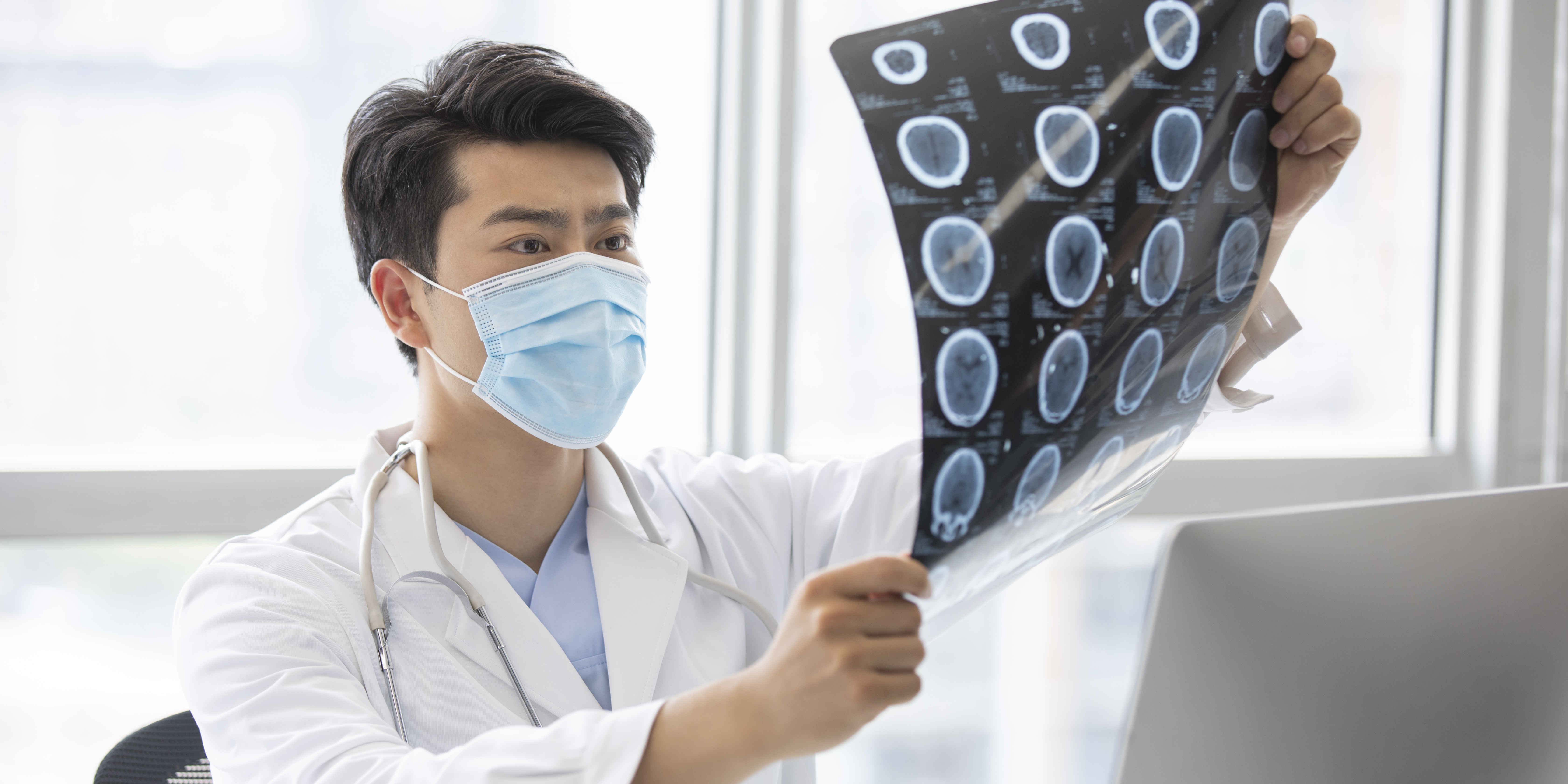
Diagnostic testing is often necessary to accurately diagnose a patient's musculoskeletal condition or injury before developing a treatment plan. Following are imaging tests that are commonly done. Read more
X-rays
X-ray is the most effective approach for diagnosing orthopaedic conditions. X-rays can be used to diagnose fractures of bones, dislocation of joints and evaluate bone density or architecture.
Computerised Tomography (CT) Scan
A CT scan creates detailed images of your body using X-rays and computer technology.
A CT scan may be requested if your doctor suspects a fracture or tumour that is not visible on an X-ray or if there is severe spinal cord or pelvis trauma.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI utilises powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed cross-sectional images of your body.
It produces excellent soft-tissue contrast, enabling the differentiation of various soft tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, muscles, and cartilage.
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
This procedure utilises x-rays to evaluate bone density. It is also known as Bone Density Scanning or Bone Densitometry.
This is a non-invasive diagnostic technique used to diagnose or assess the risk of osteoporosis and predict a person’s risk of fracture. Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones (porous bone) and increases one’s susceptibility to developing osteoporotic fractures.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
A PET scan is a whole-body scan that aids in determining the extent of bone cancer spread to other parts of the body.
During a PET scan, a radioactive tracer is injected, and images of your body are recorded using a PET scanner. A camera detects the emissions resulting from the injected radioactive tracer, and a computer then creates multi-dimensional images of the part of your body being examined.
These images provide the doctor with physiological information of the bone and are used to detect areas of abnormal bone growth associated with tumours or other abnormalities
Electromyography (EMG)
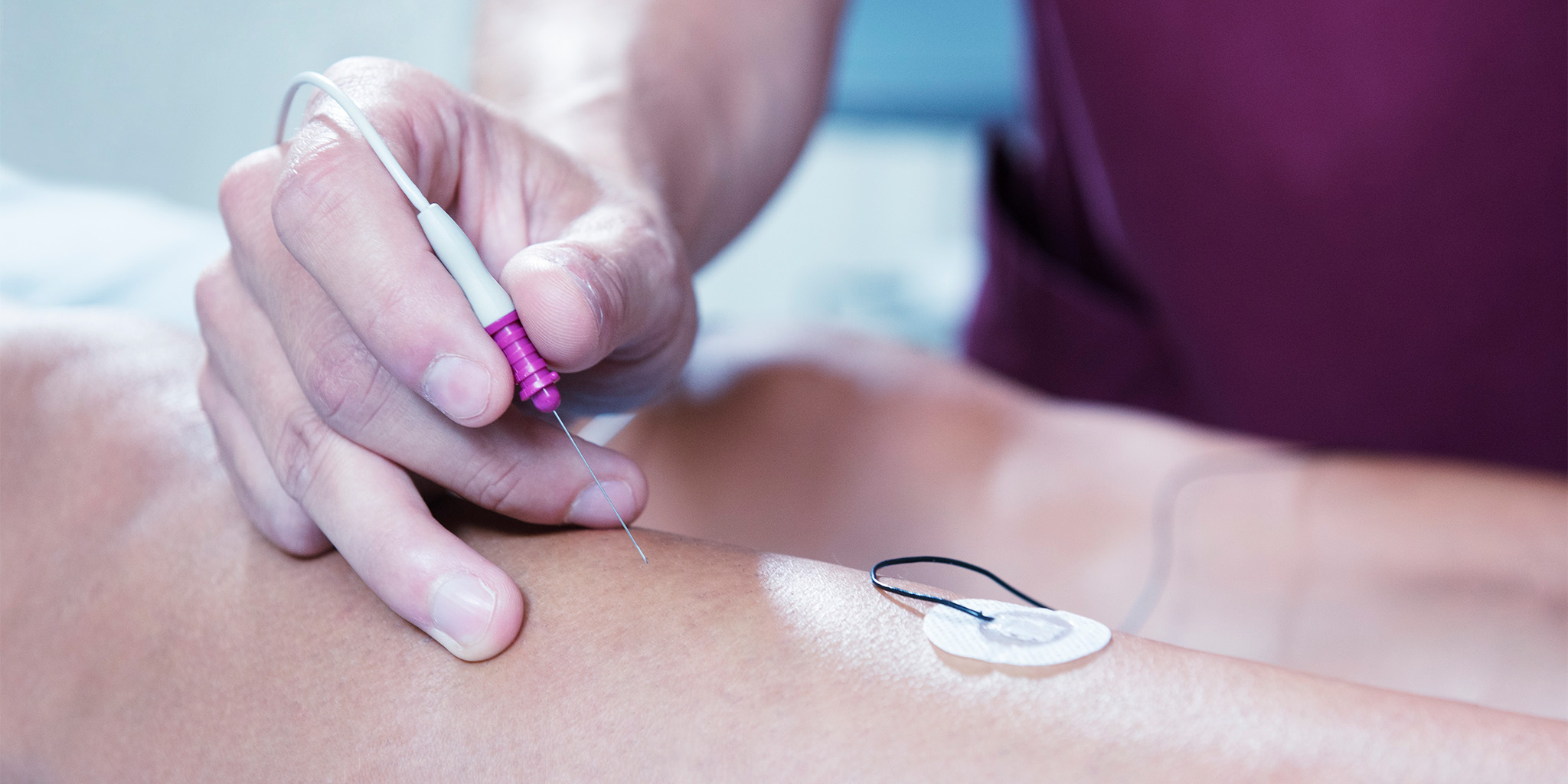
An electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the function of nerves and muscles by recording the electrical activity produced by the skeletal muscles. Read more
Electromyography is an important test used to diagnose neuromuscular disorders. It is commonly performed if an examination suggests impaired muscle strength.
Your doctor will request an electromyography testing to be done if your diagnosis suggests peripheral nervous system disorders including carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, cervical radiculopathy, lumbosacral radiculopathy, sciatica, plexopathy, or nerve injury from trauma or fractures.
Electromyography involves the insertion of a pin electrode (tiny needle) through the skin into the muscle tissue, and the electrical activity of the muscle is then recorded on a computer.
The results allow the doctor to diagnose any abnormal muscle or nerve activity. This test helps your doctor to determine if your muscle weakness is due to an injury of a nerve attached to the muscle, or if the weakness is caused by an underlying neurological disorder.
Blood Tests

Your doctor may also request various blood tests. Certain conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can be determined by the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) in your blood.
Biopsy

A small tissue sample may be removed from the affected area of your body and sent to the laboratory to be examined. There are many types of biopsies, including needle and open biopsies.
Needle biopsy involves a small incision in the skin. A special biopsy needle is inserted into the bone to get a sample. This procedure is performed under local anaesthesia.
Open biopsy involves a larger incision in the skin. A piece of bone is removed surgically. This procedure is performed under general anaesthesia.
A dedicated and expert team of Orthopaedic specialists at Pantai Hospital is available for consultation to provide the best care and assistance.
If you encounter a situation that requires medical attention, please seek immediate medical attention at the Accident and Emergency (A&E) department at your nearest Pantai Hospital.
Pantai Hospital has been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

