
Cancer treatment encompasses various modalities, each tailored to the specific needs of the individual patient and the type of cancer. These modalities include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and biological therapy, among others.
The choice of treatment or combination of treatments depends on several factors, which are carefully evaluated by a multidisciplinary team of doctors.
Factors influencing the selection of treatment options include:

Radiosurgery is a non-invasive, highly precise form of radiotherapy that delivers a concentrated dose of radiation to a targeted area. One of the key advantages of radiosurgery is its ability to deliver a highly focused beam of radiation directly to the tumour while minimising exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
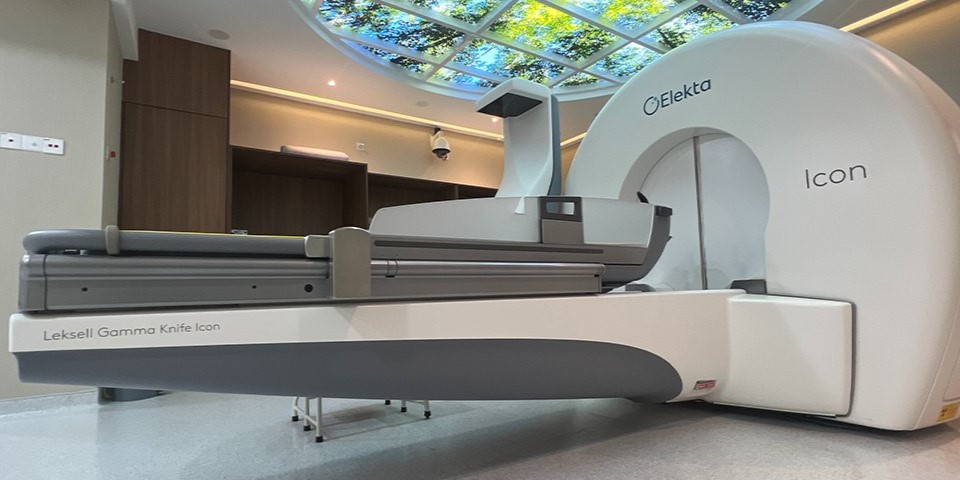
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery is a revolutionary, non-invasive procedure widely used to treat brain tumours and other neurological conditions. The term “knife” in Gamma Knife refers to the array of 192 precisely focused beams of radiation that converge on the target area within the brain.
The Leksell Gamma Knife® ICON™ is a state-of-the-art radiosurgery machine offering advanced capabilities for treating a wide range of conditions. Learn more about Gamma Knife Radiosurgery.
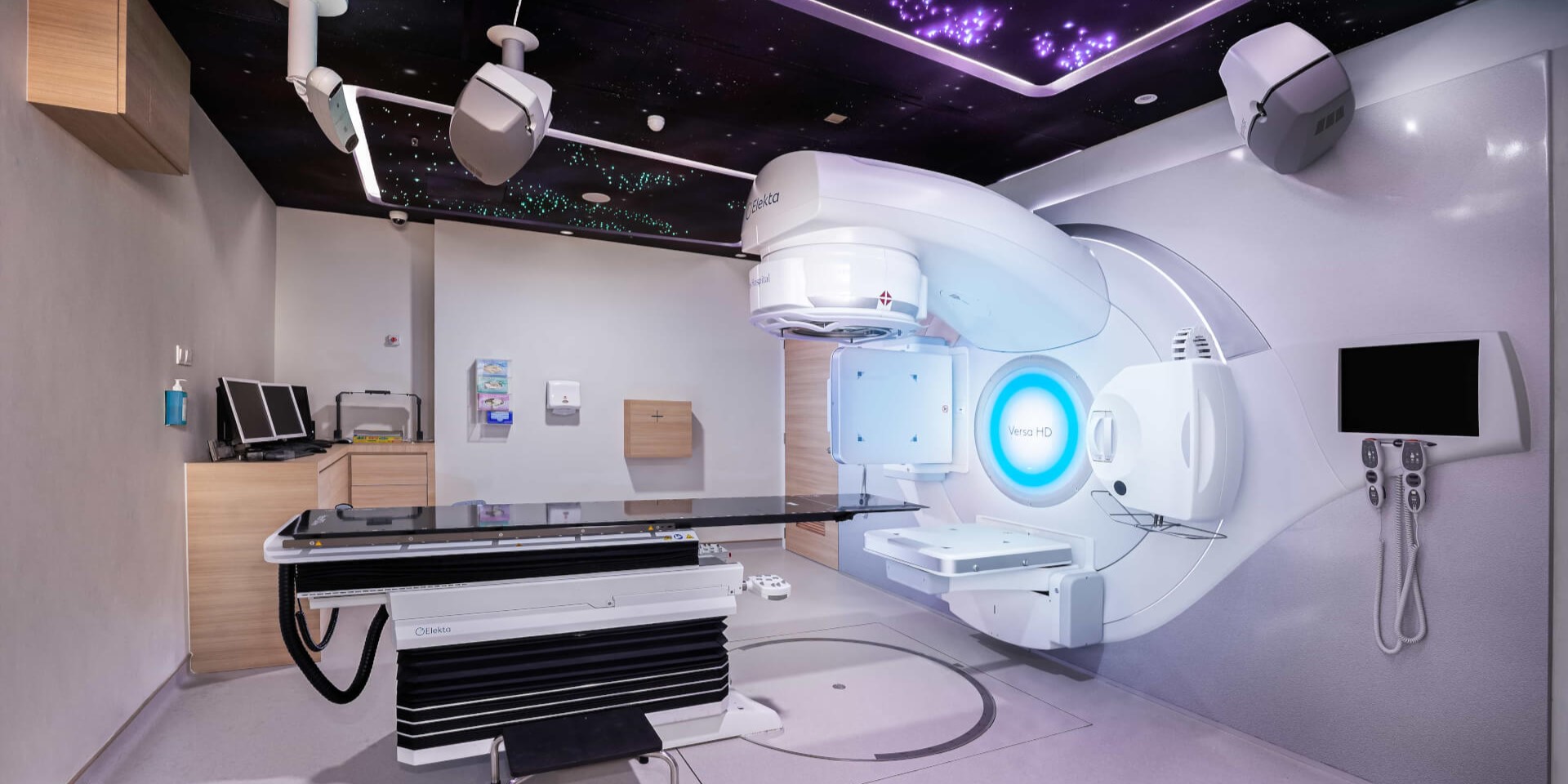
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to target and destroy cancer cells.
Types of radiation therapy provided by the Linear Accelerator (LINAC) - Elekta Versa HD machine include:
Find out more about the differences between these two cancer treatments: Chemotherapy vs Radiotherapy.
Chemotherapy is a cornerstone of cancer treatment, involving the use of powerful medications to target and destroy cancer cells. These medications, known as chemotherapy drugs or cytotoxic agents, work by disrupting the ability of cancer cells to grow and divide.
Chemotherapy is administered orally or intravenously (IV) and may be treated with one type of chemotherapy medicine or a combination of different types.
Chemotherapy treatment is often administered in multiple sessions, known as cycles, which are spaced out over a period of time. The specific schedule and duration of chemotherapy treatment depend on various factors, including the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, the chemotherapy drugs being used, and how the patient responds to treatment.
Chemotherapy may be used with other treatments to:
Learn more about ways to manage your health during chemotherapy to ensure the best outcome for your treatment.
Find out more about the differences between these two cancer treatments: Chemotherapy vs Radiotherapy.
Surgery plays a crucial role in the management of cancer, serving multiple purposes throughout the treatment process. It is indeed one of the oldest and most established forms of cancer treatment, offering benefits in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of various types of cancer.
In contrast to open surgery, Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) aims to perform surgery with minimal harm to the body by creating an access to the surgical site through the smallest incisions possible. Many cancers that required an open surgery in the past can now be treated with MIS.
MIS offers several benefits such as:
Hormone therapy, also known as endocrine therapy, involves the use of medications to either block or reduce the levels of hormones in the body. This treatment approach can effectively slow or halt the growth of cancer cells, particularly those that are hormone-sensitive.
Hormone-sensitive cancers include:
Hormone therapy can be used alongside other cancer treatments to:
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. The immune system serves as the body’s natural defence mechanism against infections and diseases, comprising white blood cells, lymph nodes, and other lymphatic organs and tissues.
Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy that utilises substances derived from living organisms to treat cancer.
Targeted therapy in cancer treatment focuses on proteins regulating the growth, division, and spread of cancer cells. This approach forms the basis of precision medicine. The majority of targeted therapies consist of either small-molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies.
The individuality of each cancer case necessitates a personalised approach to treatment. With advancements in medical technology and a deeper understanding of the disease, oncologists can tailor treatment plans to suit each patient’s specific needs. This often involves a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination thereof.
It is understandable to be overwhelmed with the vast amount of information on cancer and available treatments. Nonetheless, our advanced diagnostic and treatment technologies aim to provide the best possible outcome while minimising your side effects and recovery time.
If you experience any signs and symptoms of cancer or would like to be screened for cancer, get in touch with us to find out more about our Oncology Services at your nearest Pantai Hospital.
Our dedicated multidisciplinary team of doctors are here to guide patients through every step of their journey, from diagnosis to treatment and recovery, providing support, answering questions, and addressing concerns along the way.
Pantai Hospitals have been accredited by the Malaysian Society for Quality in Health (MSQH) for its commitment to patient safety and service quality.

